I. Introduction

The European market represents a significant opportunity for cashew nut exporters. Europe’s demand for cashew nuts is driven by their use in various food products and increasing consumer preference for healthy snack options. As this market continues to grow, understanding the regulatory and competitive landscape is crucial for successful market entry.
1. Overview of the Cashew Nut Market Relevance in Europe
Cashew nuts are popular in Europe due to their nutritional value and versatility in food applications, from snacks to culinary dishes. Europe imports a substantial volume of cashew nuts to meet consumer demand, making it a lucrative market for producers.
2. Importance of Understanding Market Entry Requirements
Entering the European market requires adherence to strict food safety and quality standards. Exporters must navigate complex regulatory frameworks, including certifications and standards for product safety, to gain market access and consumer trust. Understanding these requirements is essential for establishing a successful export business in this competitive environment.
II. Market Entry Requirements for Cashew Nuts in the European Market
1. Compliance with European Food Safety Standards

To enter the European market, cashew nuts must adhere to strict food safety standards to ensure they are safe for consumption. These standards include:
- Contaminant Controls: Cashew nuts must meet the stringent limits set for contaminants. The European Union’s Regulation (EU) 2023/915 specifies maximum levels for contaminants like mycotoxins, pesticide residues, microorganisms, and heavy metals. For example, the level of aflatoxin B1 in cashew nuts must not exceed 5 µg/kg, and the total aflatoxin content must not surpass 10 µg/kg.
- Additives and Allergens: Only approved additives are allowed in products containing cashew nuts, as specified in Regulation (EU) No 231/2012. Due to the high allergenic potential of cashew nuts, clear labeling indicating the presence of cashew nuts is mandatory to protect consumers from severe allergic reactions.
2. Mandatory Certifications and Tests
- GFSI Recognized Certifications: Cashew nut exporters to the EU should obtain certifications recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), such as BRC, IFS, or SQF. These certifications ensure that food safety practices meet international standards.
- Pesticide Residue Testing: The EU sets Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs) for pesticides, and cashew nuts must be tested to ensure compliance. Regular updates to the list of approved pesticides and new regulations, like Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/749, emphasize the control of specific chemicals like chlorates.

3. Phytosanitary Certificates and Contaminant Controls
- Phytosanitary Certificates: For certain types of cashew nuts, particularly whole, fresh ones in the green husk, a phytosanitary certificate is required when importing into the EU from third countries. This certificate verifies that the nuts have been inspected and are free from harmful pests and diseases.
- Microbiological and Heavy Metal Controls: Cashew nuts are also scrutinized for microbiological contaminants like salmonella and E. coli, which are critical public health risks. Regulation (EU) 2023/915 also sets the maximum level of cadmium for cashew nuts at 0.20 mg/kg of wet weight, except for nuts used for crushing and oil refining.
By meeting these requirements, cashew nut exporters can ensure their products are eligible for the European market, safeguarding public health and complying with regulatory standards. This not only protects consumers but also enhances the marketability of their products within Europe.
III. Additional Market Requirements for Cashew Nuts
1. Quality Requirements
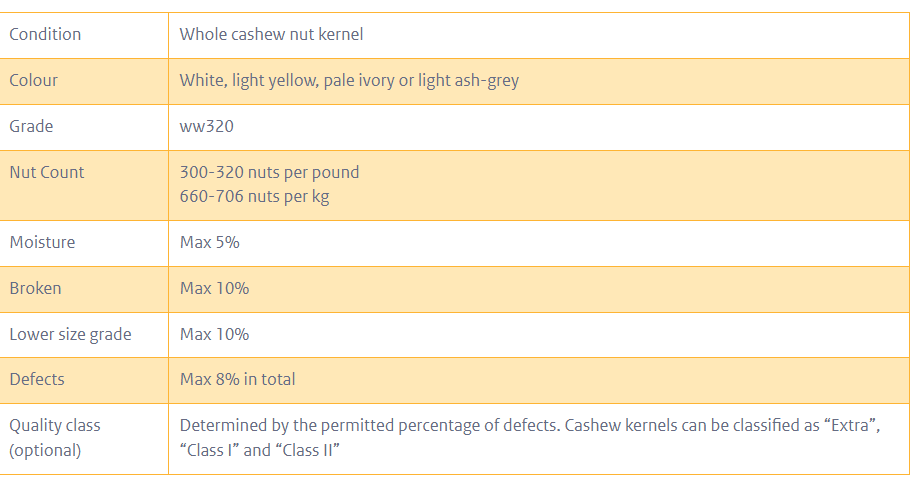
Cashew nut kernels must meet specific quality standards to satisfy European buyers. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) provides a widely accepted standard in Europe, despite the lack of specific EU standards. Key quality attributes include:
- Size and Grade: Cashew kernels are categorized based on size, with labels such as W450, W320, indicating fewer kernels per pound and thus larger size, which is typically associated with higher quality.
- Defects: Quality is also assessed by the presence of defects, such as broken pieces or damage by insects. For instance, whole nuts are preferred over broken ones, and nuts without any discoloration (black or brown spots) are considered of superior quality.
- Moisture Content: A maximum moisture content of 5% is a general requirement to prevent mold and ensure freshness.
2. Food Safety Certification
Food safety certification is crucial for cashew nut importers in Europe, even though not explicitly mandated by legislation. Most importers require one of the certifications recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), including:
- International Featured Standards (IFS)
- British Retail Consortium Global Standards (BRCGS)
- Food Safety System Certification (FSSC 22000)
- Safe Quality Food Certification (SQF)

Exporters need to ensure their certifications are up-to-date and recognized under the latest GFSI benchmarking requirements. Different certifications might be preferred by buyers in various countries, influenced by historical or operational preferences.
3. Packaging Requirements
Packaging plays a significant role in preserving the quality of cashew nuts during transit and storage:
- Common Packaging Types: Exported cashews are often packed in 10 kg to 25 kg polybags or flexi packs, with some opting for airtight tins for enhanced preservation.
- Vacuum Sealing: To extend shelf life, bags are vacuum-sealed, with air replaced by inert gases like carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
- Container Optimization: Packaging is designed to optimize container and pallet space, crucial for reducing shipping costs and ensuring the nuts’ protection during transport.

4. Labelling Requirements
Labelling is rigorously regulated to ensure consumer safety and compliance with trade standards:
- Bulk Packaging: Labels on bulk packages typically include the product name, quality, grade, and crop year. Essential storage instructions must be visible to maintain the product’s high oil content.
- Origin Labelling: European regulations require clear labelling of the product’s origin, which is particularly important for traceability and consumer information.
- Retail Packaging: For retail sales, the EU’s regulation on the provision of food information to consumers mandates clear allergen labelling (cashews are recognized as a common allergen), nutrition labelling, and legibility requirements.
By understanding and adhering to these additional buyer requirements, cashew nut exporters can significantly enhance their marketability and maintain compliance with European standards, ultimately fostering successful business relationships with European importers.
IV. Requirements for Niche Markets in the Cashew Nut Industry
1. Organic Cashew Nuts

To market cashew nuts as organic within Europe, adherence to the stringent requirements set forth by European organic legislation is essential:
- Certification Process: Organic cashew nuts must be grown and processed using certified organic methods. Before marketing products as organic in Europe, the production facilities must be audited and certified by an accredited certifier. Only after passing these audits can the European Union’s organic logo, and possibly other relevant organic standards’ logos (like Soil Association or Naturland), be displayed on products.
- Regulatory Compliance: The EU’s organic legislation, updated in January 2022, enhances the control systems and extends the range of products that can be marketed as organic. This new regulation aims to strengthen consumer trust by ensuring that both locally produced and imported organic products meet the same stringent standards.
- Electronic Certificate of Inspection: Every batch of imported organic cashew nuts must be accompanied by an electronic certificate of inspection (e-COI) to ensure compliance with EU standards.
2. Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Certification

Sustainability certifications are increasingly critical for cashew nut exporters aiming to appeal to ethically conscious consumers:
- Certification Schemes: The Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance are among the most prevalent sustainability certifications in the cashew nut industry. Fairtrade specifically caters to small-scale producer organizations and includes stipulations on worker protection, terms of payment, and a Fairtrade Minimum Price.
- Sustainable Nuts Initiative: Launched by a consortium of European companies in 2015, this initiative focuses on improving conditions in nut-producing countries and promoting sustainable sourcing practices. Participation in such initiatives can be a significant selling point for European buyers.
- Ethical Standards: Many companies also require adherence to their specific codes of conduct or widely recognized standards such as the Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit (SMETA), which evaluates labor rights, health & safety, environmental practices, and business ethics.
3. Ethnic Certification
Targeting ethnic niche markets can open additional avenues for cashew nut sales, especially within communities observing religious dietary laws:
- Halal Certification: With the growing Muslim population in Europe, projected to reach over 7% by 2050, Halal certification can significantly enhance market access. Certification ensures that the cashew nuts comply with Islamic dietary laws, increasing their appeal in Muslim-dominated countries. Bodies like Halal Certification Services (HCS) provide these certifications, which are essential for entering these markets.
- Kosher Certification: Similar to Halal, Kosher certification caters to Jewish consumers by ensuring that cashew nuts meet Jewish dietary laws. Organizations such as the Kosher London Beth Din (KLBD) offer guidelines and certification services, making products suitable for Jewish markets.
By meeting the requirements for these niche markets, cashew nut exporters can significantly broaden their consumer base, appealing to segments that value organic production, sustainability, and adherence to religious dietary standards. This not only aligns with global trends towards more ethical consumption but also opens up lucrative market segments that are increasingly influential in the global trade landscape
V. Segmentation of the European End-Market for Cashew Nuts
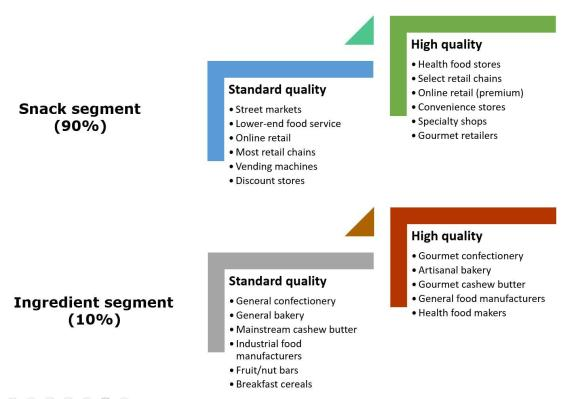
1. Snack Segment
The snack segment is the primary market for cashew nuts in Europe, accounting for approximately 90% of imported cashew nut kernels. This segment primarily enjoys cashew nuts as:
- Roasted and Salted Snacks: Roasted salty snacks dominate the cashew snacking scene in Europe. These snacks cater to a broad audience seeking convenient and tasty options.
- Health-Focused Alternatives: Following the health and wellness trend, there is a growing demand for unsalted, slow-roasted, dry-roasted, and even unroasted cashew nuts. These options are perceived as healthier alternatives to traditional salted snacks.
- Flavor Innovations: The industry is continually developing new roasting flavors and coatings (both salty and sweet) to diversify offerings and cater to evolving consumer taste preferences. The variety includes natural, spiced, and mixed nut options, expanding the appeal to a wider audience.
- Market Influences: The snacking segment’s dynamics are influenced by several factors, including economic conditions such as inflation, as well as lifestyle trends like hybrid working models leading to more at-home snacking occasions. Despite challenges like supply chain disruptions and high inflation, the resilience in consumer spending is bolstered by the growing importance of health in daily nutrition.
2. Ingredient Segment
Though smaller compared to the snack segment, the ingredient segment holds significant potential and accounts for about 10% of the European cashew market. Cashew nuts are increasingly utilized by the food processing industry in various applications:
- Confectionery: In the confectionery industry, cashew nuts are used whole or in pieces to create chocolate-coated snacks and other sweets. This follows the successful model of chocolate-coated almonds, with innovations like caramel-coated cashew kernels gaining popularity.
- Bakery: Cashew nuts are used both split and whole in bakeries, often as toppings or fillings in cookies, pastries, and other baked goods.
- Nut Spreads and Butters: There is a growing trend toward cashew nut spreads and butters, marketed as healthier alternatives to traditional peanut butter. These products often come in various flavors, enhancing their appeal.
- Breakfast Cereals: The breakfast cereals sector is incorporating cashew nuts into nut-rich granola products, responding to consumer demand for nutritious and satisfying options.
- Protein and Fruit-Nut Bars: As a healthier snacking alternative, protein and fruit-nut bars that incorporate cashew nuts are becoming more prevalent. These bars offer a good source of plant protein and align with the trend toward healthier snack options.
- Ready Meals and Sauces: Cashew nuts find a place in ready meals and sauces, such as pesto, where they serve as a cost-effective alternative to more expensive nuts like pine nuts.

The European market for cashew nuts is robust, with clear segmentation between snacks and ingredients. Each segment has distinct consumer bases and uses that drive the demand for different qualities and types of cashew nuts. Understanding these market segments helps producers and suppliers better tailor their products and marketing strategies to meet specific consumer needs and preferences, potentially leading to increased market share and revenue
VI. Overview of the Distribution Channels for Cashew Nuts in the European Market
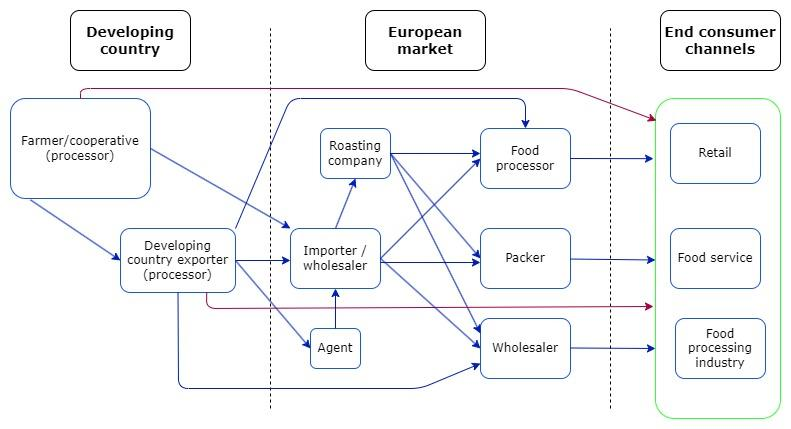
The European market for cashew nuts offers various channels through which cashew nuts are distributed, each catering to different segments of the market and having specific requirements. Understanding these channels is crucial for suppliers aiming to enter or expand within the European market. Here’s a breakdown of the primary channels:
1. Importers/Wholesalers
Importers and wholesalers play a pivotal role as the main conduit for cashew nuts entering the European market. They often have:
- Processing and Packing Facilities: Many importers own facilities where they can process and pack cashew nuts, directly supplying the retail and food service channels.
- Market Influence: These entities face significant pressure from the retail sector, which demands not only competitive pricing but also value-added products like organic or fair-trade certified nuts.
- Key Players: Companies like August Töpfer & Co. (ATCO) and Olam International are significant players, with direct sourcing and processing capabilities in cashew-producing countries.
2. Agents/Brokers
Agents and brokers act as intermediaries in the cashew nut trade, facilitating transactions between European buyers and global sellers. They:
- Charge Commissions: Typically, they charge a commission for their services, which ranges from 2% to 4%.
- Provide Private Label Services: They also help in sourcing and packaging for private labels required by European retail chains, a complex process often out of reach for smaller or less equipped exporters.
3. Retail Channel

The retail channel, while a major consumer of packaged cashew nuts, often does not engage directly with exporters from developing countries due to stringent quality and logistic requirements. Key aspects include:
- Market Dynamics: The market is increasingly polarized, with shifts towards either discount or premium segments.
- Major Retailers: Prominent players include Schwartz Gruppe, Carrefour, and Tesco, among others, with several forming buying alliances to coordinate purchasing operations across Europe.
4. Food service Channel
This channel caters to establishments like hotels, restaurants, and caterers, requiring specific product formats:
- Packaging Requirements: Cashew nuts in the food service sector are often needed in smaller packages ranging from 1kg to 5kg, contrasting with the bulk requirements of other channels.
- Growth Areas: There is growing demand in segments such as healthy fast food, international cuisines, and street food establishments.
VII. Most Interesting Channel: Importers/Wholesalers
For new exporters targeting the European market, the channel of importers and wholesalers is particularly intriguing due to several reasons:
- Market Knowledge: These importers have a deep understanding of market trends and maintain close monitoring of developments in cashew-producing countries.
- Relationship Potential: Building a lasting relationship with established importers can provide new exporters with crucial market entry support and ongoing advice.
- Diverse Product Handling: Importers who handle various types of nuts and dried fruits can offer more opportunities for suppliers that can diversify their product offerings.
Overall, while the retail channel may seem attractive due to its size, the complexities and investments required make it a challenging option for new entrants. Working with specialized importers and wholesalers provides a more accessible and supportive pathway into the European market, making it the most interesting and strategic channel for new suppliers aiming to establish a foothold and grow their presence in Europe.
VIII. Vietnam’s Dominance in the European Cashew Nut Market
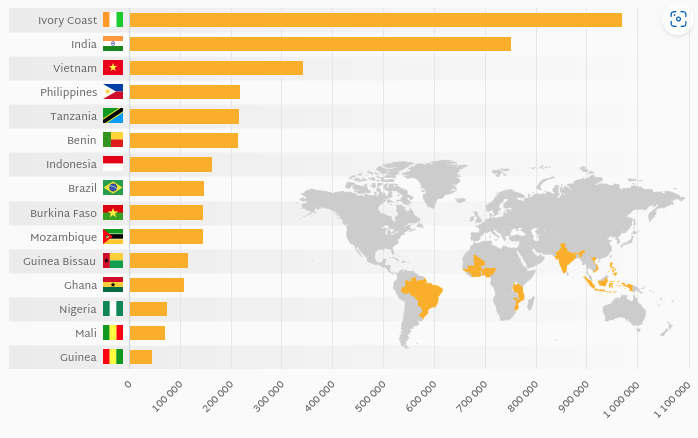
Vietnam stands as the preeminent leader in exporting cashew nut kernels, not only to Europe but globally. In 2022, Vietnam claimed the title of the top exporter, responsible for approximately two-thirds of the world’s cashew exports, with major markets including the USA, the European Union, the UK, and China. Despite its lower production compared to other countries like Côte d’Ivoire, India, and Cambodia, Vietnam’s substantial export volumes are supported by its extensive shelling capacity.
In the 2022-2023 period, Vietnam’s cashew crop was substantial, with a reported yield of 103,500 tonnes, as per the latest statistics from the International Nut and Dried Fruit Council (INC). The country compensates for its lower production by importing raw in-shell cashew nuts, primarily from Cambodia, Côte d’Ivoire, and other nations such as Ghana, Nigeria, Tanzania, Senegal, and Indonesia. Notably, Vietnamese imports from Côte d’Ivoire have decreased due to the expansion of processing capacities there, while imports from Cambodia are on the rise, reflecting increased investments by Vietnamese processors in the Cambodian cashew industry.
The logistics of importing cashew nuts from West Africa are facilitated by major shipping firms, with CMA CGM providing dedicated fortnightly shuttle services from West Africa to major markets like India and Vietnam, ensuring a steady supply throughout the cashew season.
Despite its strong export focus, where around 95% of its cashew kernels are sent abroad, Vietnam’s domestic consumption remains minimal. In 2021, Vietnam exported approximately 456,000 tonnes of cashew kernels. The United States was the largest market, followed by Europe, which received about 30% of the exports. The Vietnamese cashew exports to Europe showed a robust annual growth of 9.2%, totaling 134,000 tonnes in 2022. The forecast for exports to Europe remains optimistic, with expectations of continued high single-digit growth rates.
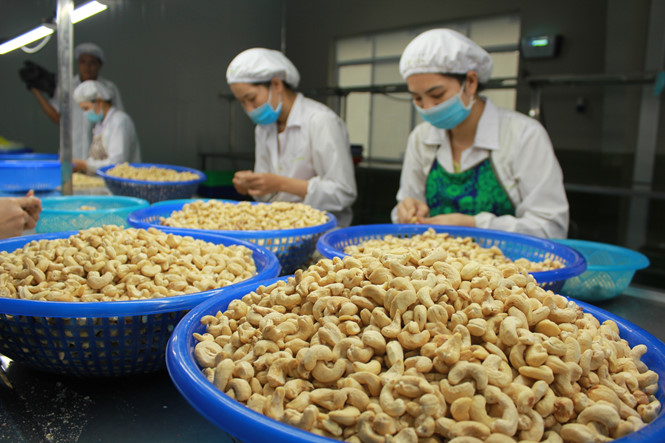

Binh Phuoc province, known as the “cashew nut capital” of Vietnam, is a significant area for cashew production. The province boasts 141,595 hectares dedicated to cashew crops and produces over 200,000 tonnes of raw cashews annually. Nearly 300 companies in Binh Phuoc are engaged in cashew processing, with several also involved in the export business.
In recent years, Vietnam has seen a shift from manual to mechanized cracking of cashews due to labor shortages, enhancing efficiency in processing. The Vietnamese Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) not only fosters domestic production but also collaborates with Cambodia to secure reliable sources for its processing industry. The Vietnam Cashew Association (VINACAS) promotes technological advancement and marketing efforts, while the Vietnam Trade Promotion Agency bolsters the country’s cashew export activities.
Vietnam’s strategic investments in processing capabilities and international collaborations underscore its pivotal role in the global cashew market, particularly in catering to European demand.
IX. Conclusion
The European market presents a dynamic and promising landscape for cashew nut exporters, underpinned by a growing consumer preference for healthy snacks and the versatility of cashew nuts in various culinary applications. As exporters navigate this lucrative market, understanding and adhering to the stringent regulatory requirements is paramount. This not only ensures compliance but also builds trust among European consumers, enhancing the marketability of their products.
Strict food safety standards, necessary certifications, and detailed packaging and labeling requirements define the entry and successful participation in the European market. Exporters must meet these standards to not just enter the market but to thrive within it, ensuring their products are both safe and appealing to the European palate.
Moreover, the market’s segmentation into snack and ingredient sectors, along with niche markets like organic, sustainable, and ethically certified products, offers exporters multiple avenues to diversify their offerings and tap into various consumer segments. This segmentation highlights the need for tailored strategies that align with the specific preferences and requirements of each segment, thereby maximizing the potential for growth and profitability.
Furthermore, the role of Vietnam as a dominant player in the global cashew market, particularly in Europe, exemplifies the importance of strategic market positioning and investment in processing capabilities. Vietnam’s model of leveraging extensive shelling capacity and robust export strategies provides valuable insights for other producers aiming to enhance their presence in international markets.
In conclusion, the European cashew nut market, with its diverse consumer base and strict standards, offers significant opportunities for exporters. By strategically navigating the regulatory landscape, embracing market segmentation, and investing in quality and sustainability, exporters can effectively expand their footprint in Europe and capitalize on the growing demand for this versatile nut.

#ProsiThangLong #Prosi #GlobalTrade #VietnamSpices #VietnamNuts #Pepper #Cashew #Cinnamon #Coconut #StarAnise #VietnamExporter
——————————-
𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐬𝐢 𝐓𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐠 𝐋𝐨𝐧𝐠 – 𝐒𝐩𝐢𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐍𝐮𝐭𝐬 𝐕𝐢𝐞𝐭𝐧𝐚𝐦 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐫 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐄𝐱𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫
🏢 𝐀𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬: 4th Floor, Kim Anh Building, No 78 Duy Tan, Cau Giay, Ha Noi
📨 𝐄𝐦𝐚𝐢𝐥: Sales@prosi.com.vn
📞 𝐎𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐞 𝐇𝐨𝐭𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐞: (+84) 9858 17797
𝐘𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐧𝐞𝐫 𝐢𝐧 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐢𝐮𝐦 𝐬𝐩𝐢𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐧𝐮𝐭𝐬



